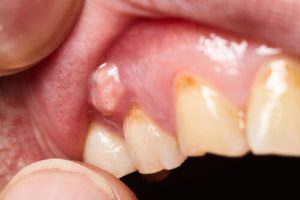
One of the most distressing symptoms of an abscessed tooth is the noticeable swelling it causes in the face. This condition not only affects your comfort and appearance but also signals a need for prompt dental care. Delve into understanding why swelling occurs and how to reduce swelling in the face from an abscessed tooth. Discover proven strategies to alleviate it while safeguarding your overall dental health.
Stay tuned to uncover practical tips to help you effectively manage and reduce facial swelling, ensuring you don’t miss the critical steps for a faster and safer recovery.
Understanding Abscessed Teeth Causes
An abscessed tooth is primarily caused by a bacterial infection within the tooth’s pulp. This severe dental condition results from several potential factors compromising oral health and allowing bacteria to establish an infection.
Tooth Decay: Deep cavities allow bacteria to reach the tooth’s inner layers, leading to infection.
Gum Disease: Infections from gum disease can extend into the roots of the teeth, creating abscesses.
Dental Trauma: Chips or cracks in teeth can permit bacteria to enter and infect the pulp.
Previous Dental Work: Sometimes, dental procedures can inadvertently introduce bacteria deep within the tooth or may weaken the tooth’s defense against infection.
Symptoms of Abscessed Teeth
An abscessed tooth represents a critical dental condition where an infection leads to the accumulation of pus inside the teeth or gums. This condition is primarily caused by bacterial infection, and recognizing its symptoms early is essential for timely and effective treatment to prevent the escalation of the infection.
Severe, Persistent Toothache
The pain resulted from an abscessed tooth is intense and continuous. It is characterized by a throbbing or sharp ache that may radiate to other parts of the face, such as the jawbone, neck, or ear. This throbbing pain might worsen when lying down due to increased pressure on the tooth.
Sensitivity to Hot and Cold
Patients often experience heightened sensitivity to extreme temperatures. Consuming hot beverages or cold foods can trigger or intensify the pain, which lingers even after removing the stimulus.
Swelling in the Face or Cheek
This swelling indicates that the infection may be spreading beyond the immediate area of the tooth. In severe cases, the swelling can expand to the eye or neck, depending on the location of the abscess.
Tender, Swollen Lymph Nodes
The lymph nodes present under the jaw or neck may become tender and swollen. This is a natural immune system response as it attempts to contain the infection.
Fever
The presence of fever is a common systemic response to infection, including dental abscesses. It signifies that the body is actively fighting the bacterial infection.
Foul Taste and Bad Breath
Pus leaking from the abscess can cause a bad taste you can feel in your mouth or persistent bad breath. This symptom is often associated with a significant infection that requires immediate care.
Immediate Actions to Reduce Swelling at Home
When dealing with an abscessed tooth, immediate home remedies can help alleviate swelling before professional dental treatment is obtained. These measures are intended to manage symptoms and are not a substitute for dental care but can provide significant relief.
Cold Compresses: Putting a cold compress or ice pack to the affected area can alleviate swelling and numb pain. To avoid tissue damage from prolonged cold exposure, this should be done in intervals—20 minutes on, followed by 20 minutes off.
Elevate Your Head: Keep your head elevated above your heart while resting or sleeping. This positioning helps reduce the blood flow to the swollen area, minimizing inflammation and discomfort.
Avoid Heat: While cold compresses are beneficial, applying heat can worsen swelling and should be avoided as it may promote bacterial growth.
Stay Hydrated: Flush the bacteria from your mouth and keep your immune system functioning properly by drinking plenty of water.
How to Reduce Swelling in Face from Abscess Tooth
When dealing with facial swelling caused by an abscessed tooth, prompt action can help manage the symptoms effectively at home while preparing for a visit with a dentist in Bundaberg at Harris Dental Boutique clinic. Here are some detailed steps to help reduce the swelling and alleviate discomfort:
Apply Cold Compresses: Putting ice packs or cold compresses on your face where the swelling is evident. Make the ice wrapped in cloth to avoid direct skin contact and apply it intermittently—20 minutes on followed by 20 minutes off—to reduce swelling and numb the pain without causing frostbite.
Elevate Your Head: When lying down, keep your head elevated above the level of your heart. This position helps decrease the blood flow to the facial area, reducing the pressure and swelling.
Saltwater Rinses: Dissolve one Tsp. of salt in a cup of water and then, wash your mouth with it. This helps cleanse the infected area, reduce the bacterial load, and soothe inflamed tissues. Perform the rinse several times daily, especially after meals and before bed.
Avoid Heat Application: Avoid using hot compresses or pads on the swollen area. Heat can increase circulation to the area, potentially worsening the swelling and spreading the infection.
Maintain Hydration: Drink enough water throughout the day. Staying hydrated helps dilute the concentration of bacteria in the saliva and assists your immune system in fighting off infection.
Limit Physical Activity: Reduce strenuous activities as increased heart rate and blood pressure from physical exertion can exacerbate swelling and lead to further discomfort.
Medical Treatments for Dental Abscesses
Dealing with a dental abscess requires professional medical intervention to prevent the spread of infection and address the underlying cause effectively. Here are a few drops of the primary medical treatments used to manage and resolve dental abscesses:
Antibiotics: If the infection in the tooth is severe or spreading to other areas, your dentist may prescribe some types of antibiotics to help fight the bacteria. Antibiotics are crucial if the infection has spread beyond the abscessed area or if you have a weakened immune system.
Drainage of the Abscess: The most direct treatment for a dental abscess is draining the pus, which contains the infection. Your dentist will start by making a tiny incision in the abscess to let the pus escape, and then cleanse the area with a saline solution to ensure it is thoroughly clean.
Root Canal Treatment: To preserve the affected tooth and eliminate the infection, a root canal may be performed. During this procedure, the dentist drills into the tooth, removes the infected central tissue (pulp), and then fills and seals the remaining space to prevent further infection.
Tooth Extraction: Extraction may be mandatory if the tooth cannot be saved. Removing the tooth alleviates the pain and drains the abscess, providing relief.
Follow-Up Care: After initial treatment, follow-up appointments are crucial to ensure the infection is completely resolved and to implement further preventive measures. This may include additional cleanings and checkups.
Pain Management: Pain relief measures, such as non-perscribed pain medications, are often recommended to help manage discomfort associated with an abscess.
Pain Management Techniques During Recovery
Recovering from dental abscess treatment can be uncomfortable due to the residual pain and swelling associated with the procedures used to clear the infection. Here are several effective pain management techniques that can help ease this discomfort during the recovery phase:
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen (Tylenol) are typically recommended to manage pain and reduce inflammation. These should be used according to the dosage instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
Cold Compresses: Applying a cold compress to the outside of your face near the affected area can help reduce swelling and numb the discomfort. It is advisable to apply the compress for 15-20 minutes every hour as needed.
Saltwater Rinses: Rinsing your mouth with a warm saline solution can soothe sore gums and alleviate mild pain.
Soft Diet: Eating soft foods that require minimal chewing can prevent further irritation of the affected area and help reduce pain. Steer clear of hard, sticky, or spicy foods that could exacerbate the pain.
Proper Oral Hygiene: Continue gently brushing your teeth and gums, avoiding the direct area of the abscess if it’s too tender. Keeping your mouth clean is needed to prevent further infections and promote healing.
Avoid Tobacco and Alcohol: Tobacco use and alcohol can both hinder wound healing and process and exacerbate pain, so it is beneficial to avoid these substances during the recovery period.
The Role of Antibiotics in Treating Abscessed Teeth
Antibiotics are crucial in treating abscessed teeth, particularly in managing the bacterial infections that cause them. Here’s how antibiotics contribute to the treatment process:
Targeting the Infection: Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria responsible for the infection. This helps reduce the infection’s spread and severity, which is vital for preventing further complications, like spreading infection to other parts of the body.
Reducing Symptoms: By combating the infection, antibiotics can significantly reduce symptoms associated with dental abscesses, such as pain, swelling, and fever. This provides relief to the patient while the body heals.
Preparing for Dental Procedures: In some cases, dentists prescribe antibiotics before performing dental procedures like a root canal or tooth extraction. This pre-treatment helps to minimize the risk of bacteria spreading during the procedure.
Complementing Other Treatments: Antibiotics are often used with other dental treatments. While they do not replace the need for procedures that physically address the source of the tooth infection (like draining the abscess or removing the infected tooth), they support the overall treatment regimen.
Preventing Recurrence: For severe or recurring abscesses, antibiotics help prevent future infections by reducing the presence of harmful bacteria around the affected site.
When to See a Dentist: Recognizing Emergency Signs
Identifying the emergency signs of dental issues can mean the difference between simple treatment and severe complications. Here are some critical indicators that require immediate dental attention:
Severe Pain: If you experience intense, persistent pain that does not subside with over-the-counter pain relievers, you must visit a dentist immediately. Severe pain may indicate an advancing infection or other serious conditions.
Swelling: Significant swelling in the face, neck, or cheeks, especially if it spreads or is accompanied by redness, is a clear signal that urgent dental care is needed. A swollen face can sometimes indicate an infection spreading beyond the initial site.
Fever: A fever combined with dental pain or swelling is often a sign of infection. Fever indicates your body’s response to fight the infection; medical intervention is crucial to manage it effectively.
Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: If swelling from an abscess or infection impinges your ability to breathe or swallow, it can become a life-threatening emergency. Immediate medical care is necessary in such cases.
Persistent or Prolonged Bleeding: While some bleeding is expected after a dental procedure if it persists for more than 24 hours, it’s vital to see your dentist. Persistent bleeding can be a sign of a complication from the procedure or an underlying condition.
Unpleasant Tastes or Persistent Bad Breath: A foul taste or chronic bad breath, despite proper oral hygiene, can indicate an infection or decay that needs professional treatment.
Broken Tooth or Dental Trauma: If you suffer a dental injury that results in a broken tooth or trauma to your gums, seeking immediate dental care can prevent further damage and reduce the risk of long-term issues.
Preventing Future Dental Abscesses: Oral Hygiene Tips
Proper oral hygiene is mandatory for preventing dental abscesses and ensuring long-term dental health. Here are essential tips to help you avoid future dental abscesses:
Regular Brushing and Flossing: Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove dental plaque and food particles that can lead to decay and abscesses.
Use Antiseptic Mouthwash: Incorporating an antiseptic mouthwash into your daily routine can help reduce bacteria that cause infections.
Routine Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and examinations. These visits can catch potential problems early before they develop into abscesses.
Avoid Sugary Foods and Drinks: Limiting sugar intake can help prevent tooth decay, a primary cause of abscesses. Opt for healthier snacks and drinks.
Don’t Ignore Dental Pain: If you experience tooth pain or sensitivity, see a dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment can prevent more serious infections like abscesses.
Protect Your Teeth: If you play sports, wear a mouthguard to safeguard your teeth from injury, which can lead to abscesses.
Quit Smoking: Smoking can debilitate your immune system and affect oral health, making you more susceptible to infections, including dental abscesses.
Managing swelling from an abscessed tooth effectively requires prompt action and proper care. Applying cold compresses, maintaining oral hygiene, and seeking immediate dental consultation can significantly reduce discomfort and prevent further health complications. While home remedies can provide temporary relief, consulting with a dentist is crucial to treat the underlying infection and ensure long-term oral health.
References
10 Home Remedies for a few Tooth Abscesses Tooth Abscess
https://www.healthline.com/health/home-remedies-for-abscess-tooth
How can you reduce facial swelling?
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-to-reduce-swelling-in-face
Abscessed Tooth: Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and More
https://www.verywellhealth.com/pain-relief-for-an-abscessed-tooth-remedies-1059316
Dental abscess
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/dental-abscess/
Tooth abscess – Symptoms & causes
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tooth-abscess/symptoms-causes/syc-20350901